Tiedosto:Langs N.Amer.png

Tämän esikatselun koko: 661 × 600 kuvapistettä. Muut resoluutiot: 265 × 240 kuvapistettä | 529 × 480 kuvapistettä | 847 × 768 kuvapistettä | 1 129 × 1 024 kuvapistettä | 1 290 × 1 170 kuvapistettä.
Alkuperäinen tiedosto (1 290 × 1 170 kuvapistettä, 599 KiB, MIME-tyyppi: image/png)
Tiedoston historia
Päiväystä napsauttamalla näet, millainen tiedosto oli kyseisellä hetkellä.
| Päiväys | Pienoiskuva | Koko | Käyttäjä | Kommentti | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nykyinen | 20. heinäkuuta 2019 kello 17.28 | 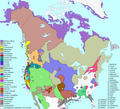 | 1 290 × 1 170 (599 KiB) | Denniss | Reverted to version as of 21:52, 1 March 2009 (UTC) |
| 13. heinäkuuta 2019 kello 16.54 |  | 1 290 × 1 170 (840 KiB) | Thylacinus cynocephalus | Having colonial borders on an indigenous language map is offensive | |
| 1. maaliskuuta 2009 kello 21.52 | 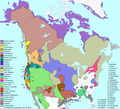 | 1 290 × 1 170 (599 KiB) | Malus Catulus | optipng, pngout | |
| 22. joulukuuta 2006 kello 14.31 |  | 1 290 × 1 170 (668 KiB) | Mahahahaneapneap | pngcrushed | |
| 11. marraskuuta 2006 kello 00.43 |  | 1 290 × 1 170 (916 KiB) | Ish ishwar | update | |
| 1. huhtikuuta 2006 kello 04.55 |  | 1 296 × 1 176 (678 KiB) | Locke Cole | smaller file (pngout /f0 Langs_N.Amer.png /b4096) / Change: -315546 bytes ( 68% of original) | |
| 7. tammikuuta 2006 kello 04.01 |  | 1 296 × 1 176 (986 KiB) | Ish ishwar | adai,chimariko = unclassified; adjust uto-aztec, salinan, southern athabasc., muskogean; + Isla Ángel de la Guarda, Isla del Tiburón, Lake Okeechobee | |
| 9. joulukuuta 2005 kello 21.24 |  | 1 318 × 1 195 (714 KiB) | Ish ishwar | checker grid pattern to Chumash | |
| 6. joulukuuta 2005 kello 06.12 | 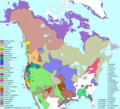 | 1 318 × 1 195 (714 KiB) | Ish ishwar | forgot seri, fix fam key | |
| 6. joulukuuta 2005 kello 01.21 |  | 1 318 × 1 195 (712 KiB) | Ish ishwar | update |
Tiedoston käyttö
Seuraava sivu käyttää tätä tiedostoa:
Tiedoston järjestelmänlaajuinen käyttö
Seuraavat muut wikit käyttävät tätä tiedostoa:
- Käyttö kohteessa af.wikipedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa an.wikipedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa ar.wikipedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa azb.wikipedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa az.wikipedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa bat-smg.wikipedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa be-tarask.wikipedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa beta.wikiversity.org
- Käyttö kohteessa be.wikipedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa bg.wikipedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa br.wikipedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa ca.wikipedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa ca.wikimedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa cs.wikipedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa cv.wikipedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa da.wikipedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa da.wikibooks.org
- Käyttö kohteessa de.wikipedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa dsb.wikipedia.org
- Käyttö kohteessa en.wikipedia.org
- History of the Americas
- North America
- Native Americans in the United States
- First Nations in Canada
- Linguistics and the Book of Mormon
- Lower Rio Grande Valley
- User:Ish ishwar
- Classification of the Indigenous languages of the Americas
- Wikipedia:Featured pictures thumbs/03
- Indigenous peoples of the Americas
- Wikipedia:Wikipedia Signpost/2005-12-26/Features and admins
- Wikipedia:Featured picture candidates/December-2005
- Wikipedia:Featured picture candidates/Indigenous language families north of Mexico
- User:Cyde/Featured pictures
- Talk:New World
- Wikipedia:Picture of the day/April 2006
- Wikipedia:POTD/April 1, 2006
- Wikipedia:Picture of the day/April 1, 2006
- Wikipedia:Today's second feature/April 1, 2006
- Portal:North America/Selected picture
- User talk:Wapcaplet/Archive 3
- Wikipedia:POTD column/April 1, 2006
- Wikipedia:POTD row/April 1, 2006
Näytä lisää tämän tiedoston järjestelmänlaajuista käyttöä.

